아두이노 적외선 레이더 만들기
2015-04-07 14:33:42
개요
레이더는 전자파를 대상물을 향해서 발사해 그 반사파를 측정하는 것으로 대상물까지의 거리나 형상을 측정하는 장치입니다.
멀리 있는 물체와의 거리를 전자파에 의해서 계측해서 전시하는 장치로 비행기의 위치를 파악하거나, 강수량 예측 시스템 등에 사용되고 있습니다.
또한 전쟁에서 적 비행기의 위치를 알아내기도 하며, 사람이 들어가지 못하는 심해까지 레이더를 쏘아 그 수심을 알아내기도 합니다.

사진 출처 : phys.org
이번 컨텐츠에서는 서보모터와 적외선 거리 센서를 이용하여 간단한 레이더를 만들어 보겠습니다.
프로세싱을 이용하여 레이더를 나타내고, 적외선 거리 센서에 측정된 거리를 이용해 레이더를 표시해 보도록 하겠습니다.
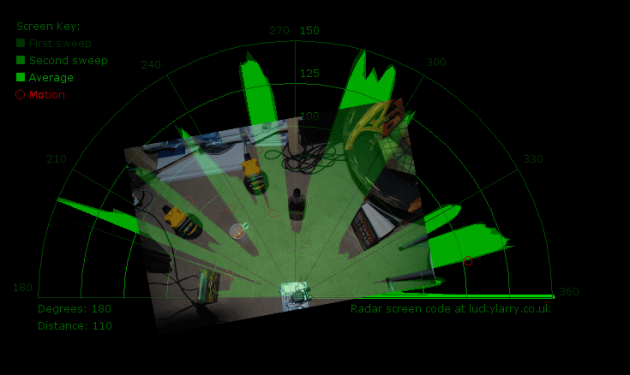
사진 출처 : luckylarry
동영상 미리 보기
시작전 개념 이해하기
부품 목록
| NO | 부품명 | 수량 | 상세설명 |
| 1 | 오렌지 보드 | 1 | |
| 2 | 서보모터 | 1 | FS5106B |
| 3 | 적외선 거리 센서 | 1 | |
| 4 | 브레드보드 | 1 | |
| 5 | 점퍼케이블 | 8 |
| 부품명 | 오렌지 보드 | 서보모터 | 적외선 거리 센서 | 브레드 보드 | 점퍼 케이블 |
| 파트 |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
하드웨어 Making
브레드보드 레이아웃
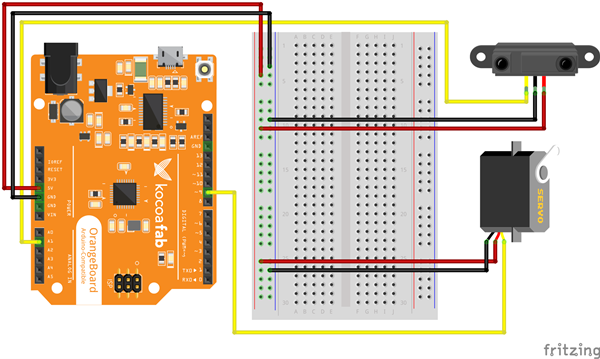
회로도
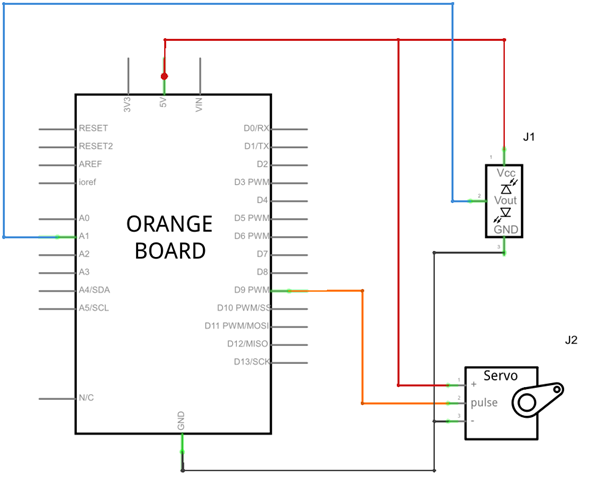
센서 연결
서보모터 위에 적외선 거리 센서를 올린 후 서보모터가 돌때 적외선 거리 센서의 방향도 같이 돌수 있도록 붙여 줍니다.
소프트웨어 Coding
아두이노 코드
/*
luckylarry.co.uk
Radar Screen Visualisation for Sharp GP2Y0A02 IR range finder
Sends sensor readings for every degree moved by the servo
values sent to serial port to be picked up by Processing
*/
#include // include the standard servo library
Servo leftRightServo; // set a variable to map the servo
int leftRightPos = 0; // set a variable to store the servo position
const int numReadings = 10; // set a variable for the number of readings to take
int index = 0; // the index of the current reading
float total = 0; // the total of all readings must be a float to allow totaling of float values
int average = 0; // the average
int IRpin = 1; // analog pin for reading the IR sensor
/* setup the pins, servo and serial port */
void setup() {
leftRightServo.attach(9);
// initialize the serial port:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
/* begin rotating the servo and getting sensor values */
void loop() {
for(leftRightPos = 0; leftRightPos < 180; leftRightPos++) { // going left to right.
leftRightServo.write(leftRightPos);
for (index = 0; index<=numReadings;index++) { // take x number of readings from the sensor and average them
float volts = analogRead(IRpin)*0.0048828125; // value from sensor*(5/1024) - if running 3.3.volts then change 5 to 3.3
float distance = 65*pow(volts, -1.10); // worked out from graph 65 = theretical distance / (1/Volts)S
total = total + distance; // update total
delay(20);
}
average = (int) total/numReadings; // create average reading CAST TO INT!! remove the decimal places
if (index >= numReadings) { // reset the counts when at the last item of the array
index = 0;
total = 0;
}
Serial.print("X"); // print leading X to mark the following value as degrees
Serial.print(180-leftRightPos); // current servo position
Serial.print("V"); // preceeding character to separate values
Serial.println(average); // average of sensor readings
}
/*
start going right to left after we got to 180 degrees
same code as above
*/
for(leftRightPos = 180; leftRightPos > 0; leftRightPos--) { // going right to left
leftRightServo.write(leftRightPos);
for (index = 0; index<=numReadings;index++) {
float volts = analogRead(IRpin)*0.0048828125; // value from sensor*(5/1024) - if running 3.3.volts then change 5 to 3.3
float distance = 65*pow(volts, -1.10); // worked out from graph 65 = theretical distance / (1/Volts)S
total = total + distance;
delay(20);
}
average = (int) total/numReadings;
if (index >= numReadings) {
index = 0;
total = 0;
}
Serial.print("X");
Serial.print(180-leftRightPos);
Serial.print("V");
Serial.println(average);
}
}
프로세싱 코드
/*
luckylarry.co.uk
Radar Screen Visualisation for Sharp GP2Y0A02
Maps out an area of what the GP2Y0A02 sees from a top down view.
Takes and displays 2 readings, one left to right and one right to left.
Displays an average of the 2 readings
Displays motion alert if there is a large difference between the 2 values.
*/
import processing.serial.*; // import serial library
Serial myPort; // declare a serial port
float x, y; // variable to store x and y co-ordinates for vertices
int radius = 350; // set the radius of objects
int w = 300; // set an arbitary width value
int degree = 0; // servo position in degrees
int value = 0; // value from sensor
int motion = 0; // value to store which way the servo is panning
int[] newValue = new int[181]; // create an array to store each new sensor value for each servo position
int[] oldValue = new int[181]; // create an array to store the previous values.
PFont myFont; // setup fonts in Processing
int radarDist = 0; // set value to configure Radar distance labels
int firstRun = 0; // value to ignore triggering motion on the first 2 servo sweeps
/* create background and serial buffer */
void setup(){
// setup the background size, colour and font.
size(750, 450);
background (0); // 0 = black
myFont = createFont("verdana", 12);
textFont(myFont);
// setup the serial port and buffer
myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[0], 9600);
myPort.bufferUntil('\n');
}
/* draw the screen */
void draw(){
fill(0); // set the following shapes to be black
noStroke(); // set the following shapes to have no outline
ellipse(radius, radius, 750, 750); // draw a circle with a width/height=750 with its center position (x and y) set by the radius
rectMode(CENTER); // set the following rectangle to be drawn around its center
rect(350,402,800,100); // draw rectangle (x, y, width, height)
if (degree >= 179) { // if at the far right then set motion = 1/ true we're about to go right to left
motion = 1; // this changes the animation to run right to left
}
if (degree <= 1) { // if servo at 0 degrees then we're about to go left to right
motion = 0; // this sets the animation to run left to right
}
/* setup the radar sweep */
/*
We use trigonmetry to create points around a circle.
So the radius plus the cosine of the servo position converted to radians
Since radians 0 start at 90 degrees we add 180 to make it start from the left
Adding +1 (i) each time through the loops to move 1 degree matching the one degree of servo movement
cos is for the x left to right value and sin calculates the y value
since its a circle we plot our lines and vertices around the start point for everything will always be the center.
*/
strokeWeight(7); // set the thickness of the lines
if (motion == 0) { // if going left to right
for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++) { // draw 20 lines with fading colour each 1 degree further round than the last
stroke(0, (10*i), 0); // set the stroke colour (Red, Green, Blue) base it on the the value of i
line(radius, radius, radius + cos(radians(degree+(180+i)))*w, radius + sin(radians(degree+(180+i)))*w);
// line(start x, start y, end x, end y)
}
} else { // if going right to left
for (int i = 20; i >= 0; i--) { // draw 20 lines with fading colour
stroke(0,200-(10*i), 0); // using standard RGB values, each between 0 and 255
line(radius, radius, radius + cos(radians(degree+(180+i)))*w, radius + sin(radians(degree+(180+i)))*w);
}
}
/* Setup the shapes made from the sensor values */
noStroke(); // no outline
/* first sweep */
fill(0,50,0); // set the fill colour of the shape (Red, Green, Blue)
beginShape(); // start drawing shape
for (int i = 0; i < 180; i++) { // for each degree in the array
x = radius + cos(radians((180+i)))*((oldValue[i]*2)); // create x coordinate
y = radius + sin(radians((180+i)))*((oldValue[i]*2)); // create y coordinate
vertex(x, y); // plot vertices
}
endShape(); // end shape
/* second sweep */
fill(0,110,0);
beginShape();
for (int i = 0; i < 180; i++) {
x = radius + cos(radians((180+i)))*(newValue[i]*2);
y = radius + sin(radians((180+i)))*(newValue[i]*2);
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape();
/* average */
fill(0,170,0);
beginShape();
for (int i = 0; i < 180; i++) {
x = radius + cos(radians((180+i)))*(((newValue[i]+oldValue[i])/2)*2); // create average
y = radius + sin(radians((180+i)))*(((newValue[i]+oldValue[i])/2)*2);
vertex(x, y);
}
endShape();
/* if after first 2 sweeps, highlight motion with red circle*/
if (firstRun >= 360) {
stroke(150,0,0);
strokeWeight(1);
noFill();
for (int i = 0; i < 180; i++) {
if (oldValue[i] - newValue[i] > 35 || newValue[i] - oldValue[i] > 35) {
x = radius + cos(radians((180+i)))*(newValue[i]*2);
y = radius + sin(radians((180+i)))*(newValue[i]*2);
ellipse(x, y, 10, 10);
}
}
}
/* set the radar distance rings and out put their values, 50, 100, 150 etc.. */
for (int i = 0; i <=6; i++){
noFill();
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(0, 255-(30*i), 0);
ellipse(radius, radius, (100*i), (100*i));
fill(0, 100, 0);
noStroke();
text(Integer.toString(radarDist+25), 380, (305-(radarDist*2)), 50, 50); // change this to measure up to 150cm
radarDist+=25;
}
radarDist = 0;
/* draw the grid lines on the radar every 30 degrees and write their values 180, 210, 240 etc.. */
for (int i = 0; i <= 6; i++) {
strokeWeight(1);
stroke(0, 55, 0);
line(radius, radius, radius + cos(radians(180+(30*i)))*w, radius + sin(radians(180+(30*i)))*w);
fill(0, 55, 0);
noStroke();
if (180+(30*i) >= 300) {
text(Integer.toString(180+(30*i)),
(radius+10) + cos(radians(180+(30*i)))*(w+10), (radius+10) + sin(radians(180+(30*i)))*(w+10), 25, 50);
} else {
text(Integer.toString(180+(30*i)), radius + cos(radians(180+(30*i)))*w, radius + sin(radians(180+(30*i)))*w, 60,40);
}
}
/* Write information text and values. */
noStroke();
fill(0);
rect(350,402,800,100);
fill(0, 100, 0);
text("Degrees: "+Integer.toString(degree), 100, 380, 100, 50);
// use Integet.toString to convert numeric to string as text() only outputs strings
text("Distance: "+Integer.toString(value), 100, 400, 100, 50);
// text(string, x, y, width, height)
text("Radar screen code at luckylarry.co.uk", 540, 380, 250, 50);
fill(0);
rect(70,60,150,100);
fill(0, 100, 0);
text("Screen Key:", 100, 50, 150, 50);
fill(0,50,0);
rect(30,53,10,10);
text("First sweep", 115, 70, 150, 50);
fill(0,110,0);
rect(30,73,10,10);
text("Second sweep", 115, 90, 150, 50);
fill(0,170,0);
rect(30,93,10,10);
text("Average", 115, 110, 150, 50);
noFill();
stroke(150,0,0);
strokeWeight(1);
ellipse(29, 113, 10, 10);
fill(150,0,0);
text("Motion", 115, 130, 150, 50);
}
/* get values from serial port */
void serialEvent (Serial myPort) {
String xString = myPort.readStringUntil('\n'); // read the serial port until a new line
if (xString != null) { // if theres data in between the new lines
xString = trim(xString); // get rid of any whitespace just in case
String getX = xString.substring(1, xString.indexOf("V")); // get the value of the servo position
String getV = xString.substring(xString.indexOf("V")+1, xString.length()); // get the value of the sensor reading
degree = Integer.parseInt(getX); // set the values to variables
value = Integer.parseInt(getV);
/*
If our values are outside either end of the sensors range then convert them to the max/min for a better display without the spikes
*/
if (value > 150) {
value = 150;
}
if (value < 20) {
value = 20;
}
oldValue[degree] = newValue[degree]; // store the values in the arrays.
newValue[degree] = value;
/* sets a counter to allow for the first 2 sweeps of the servo */
firstRun++;
if (firstRun > 360) {
firstRun = 360; // keep the value at 360
}
}
}
소프트웨어 설명
void setup(){
// setup the background size, colour and font.
size(750, 450);
background (0); // 0 = black
myFont = createFont("verdana", 12);
textFont(myFont);
// setup the serial port and buffer
myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[0], 9600);
myPort.bufferUntil('\n');
}
포트가 여러개 잡혀있을 경우, 위 프로세싱 코드중 setup() 부분에서 'myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[0], 9600);' 이부분 안에 list()[0] 안에 숫자를 바꿔 주시면 됩니다.
(ex : 포트가 3, 11, 12번이 잡혀있을 경우 아두이노가 11번 포트에 연결되있을 경우 list안에 1을 넣어주시면 됩니다. 맨 처음이 0번으로 시작됩니다.)
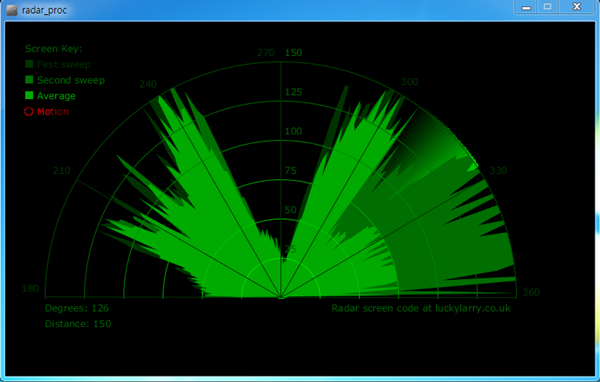
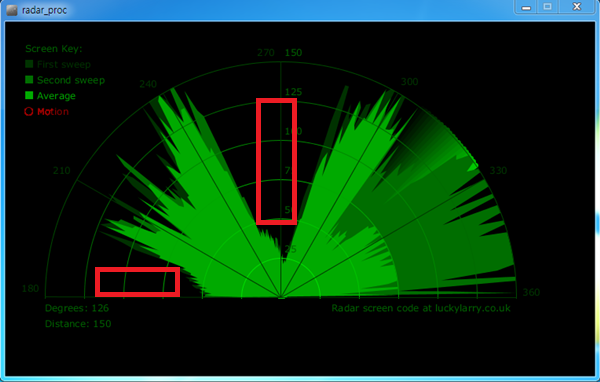
아두이노 코드를 업로드 하고, 프로세싱을 실행 하면 밑에 사진과 같이 화면이 나옵니다. 서보모터 각도에 따라 적외선 센서가 거리를 측정하고 해당 각도에 따른 거리를 프로세싱에 보내면 프로세싱에서 레이더 이미지를 계속 수정합니다.
센서 앞에 장애물이 있을 경우 레이더에서는 장애물 있는 부분이 검은색으로 나타나게 됩니다.(적외선 거리센서에 측정되는 거리를 녹색으로 표시합니다. 앞에 장애물이 있을 경우 거리가 짧게 측정되므로 녹색부분이 작아집니다.)

판다마니아
 오렌지 보드, KocoaFAB, 적외선 거리 센서, 서보 모터, Radar
오렌지 보드, KocoaFAB, 적외선 거리 센서, 서보 모터, Radar